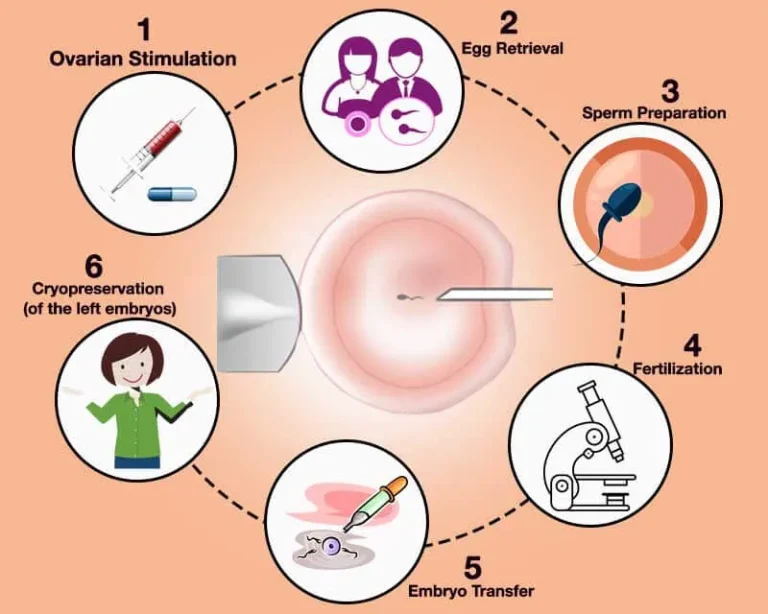
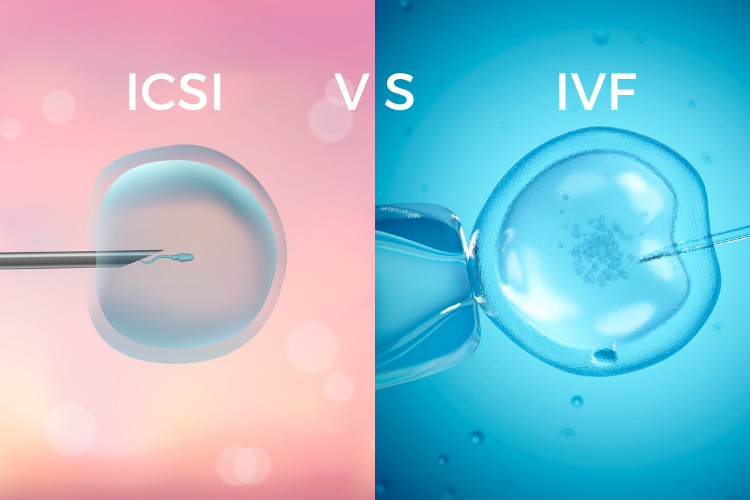
ICSI serves as a specific technique within assisted reproductive technologies (ART) and is an integral part of in vitro fertilization (IVF). This method entails the selection of a singular, potent sperm with optimal motility, directly injecting it into a fertile ovum using a micro-needle for assisted fertilization. The subsequent cultivation of the embryo in a sterile embryology laboratory leads to its development into a day-5 blastocyst. This blastocyst is then transferred to the uterus, enabling continuous growth within the womb. Recognized as a secure and highly effective medical technology, ICSI addresses male-factor infertility concerns, such as unhealthy sperm or low sperm count, as well as challenges faced by women with low egg counts, thick eggshells, or an unhealthy uterus.
 English
English
 English
English
 English
English